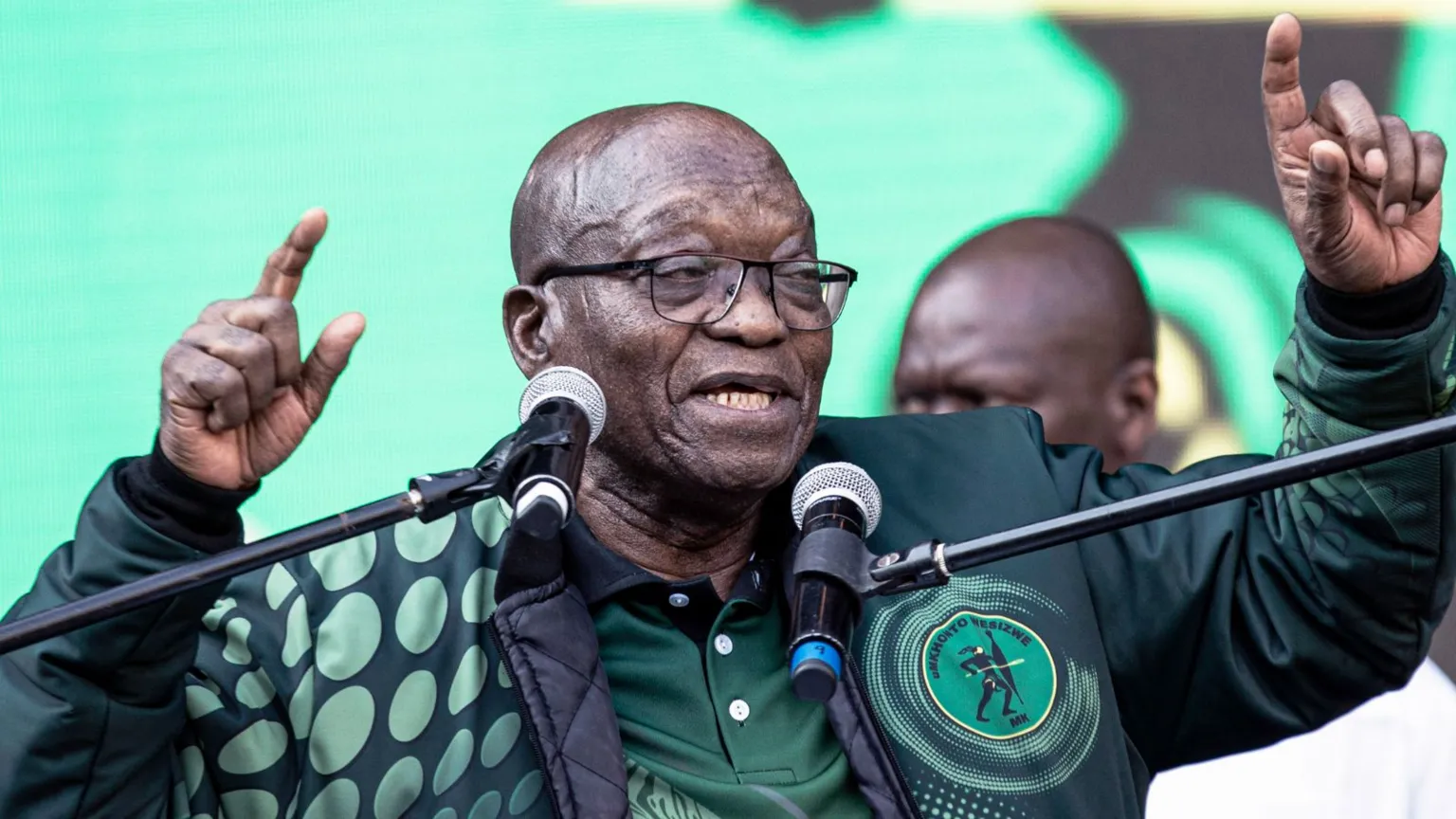
Former South African President Jacob Zuma has launched a scathing attack on some of the country’s top judges after he was barred from running for parliament on Monday.
In his first interview since the ban, Mr Zuma told the BBC the Constitutional Court was wrong to decide he was unfit to run, based on his 2021 conviction for contempt of court.
“I expected that from our judges, but they are definitely wrong. Not correct,” the 82-year-old said, adding that the constitution should be changed.
Ahead of next week’s general election, Mr Zuma had been campaigning under the banner of the newly formed uMkhonto weSizwe (MK) party.
He joined the party after falling out with the governing African National Congress (ANC), which he used to lead.
The electoral commission argued that the constitution bars anyone who was sentenced to more than 12 months in prison from serving as a lawmaker – a view backed by the Constitutional Court judges.
Mr Zuma was convicted in 2021 for refusing to testify at an inquiry investigating corruption during his presidency.
His lawyers had insisted he was entitled to become an MP as his sentence was reduced to three months after current President Cyril Ramaphosa released him from prison in what was widely seen as an attempt to placate the former president’s angry supporters.
“The judges of the Constitutional Court have acted very funny to me – towards me in particular,” Mr Zuma told the BBC.
“They are not taking into account the will of the people of this country, they use their own will.”
He was president from 2009 to 2018 before being forced out as leader of the ANC amid allegations of widespread corruption in his government.
The corruption, widely known as “state capture”, saw hundreds of millions of dollars of public assets taken into private hands. Mr Zuma has always denied any direct role in corruption, but is due to face trial next year on allegations of bribery.
He told the BBC he had been wrongly stripped of his role as leader of the ANC.
“I don’t know what ‘state capture’ means. If people say I am corrupt, what did I do? Do you have any facts about it? Am I guilty?
“I was removed before the end of my term, and nothing was produced as evidence that this was an issue.”
Mr Zuma’s MK party had previously voiced its desire to change South Africa’s constitution, which was drawn up 30 years ago at the birth of the country’s democracy following decades of white-minority rule.
Asked about this in the light of his election ban, Mr Zuma reiterated that the historic document needed to be changed.
“This constitution in the continent of Africa is guided by the laws from Europe, not us,” he said.
“There is nothing that has come right in this continent because we are still dominated by those who were the ones [who] slaved us, and after slavery, oppressed us, and after oppression, put their own laws to run us.
“There are details that clash with our lives.”
An Ipsos opinion poll released last month gave MK 8% of the vote, and the ANC 40% as it loses support to MK and other opposition parties.
But some analysts suggest that with the governing party stepping up its campaign in recent weeks, it could still cross the 50% mark. But if the ANC gets less than half of the vote, it would lose its majority for the first time in 30 years.
MK is expected to do especially well in Mr Zuma’s home region of KwaZulu-Natal.
After Mr Zuma was jailed for contempt of court in 2021, angry supporters sparked days of deadly riots. More than 300 people were killed in the clashes.
On Wednesday Mr Zuma said this violence demonstrated the scale of public support for him.
“This must tell you that the masses of this country loves Zuma – that’s why we had that,” he said.
When asked by the BBC if he would use this interview to call for peace and calm ahead of next week’s election, Mr Zuma replied: “I’ve always done so.”