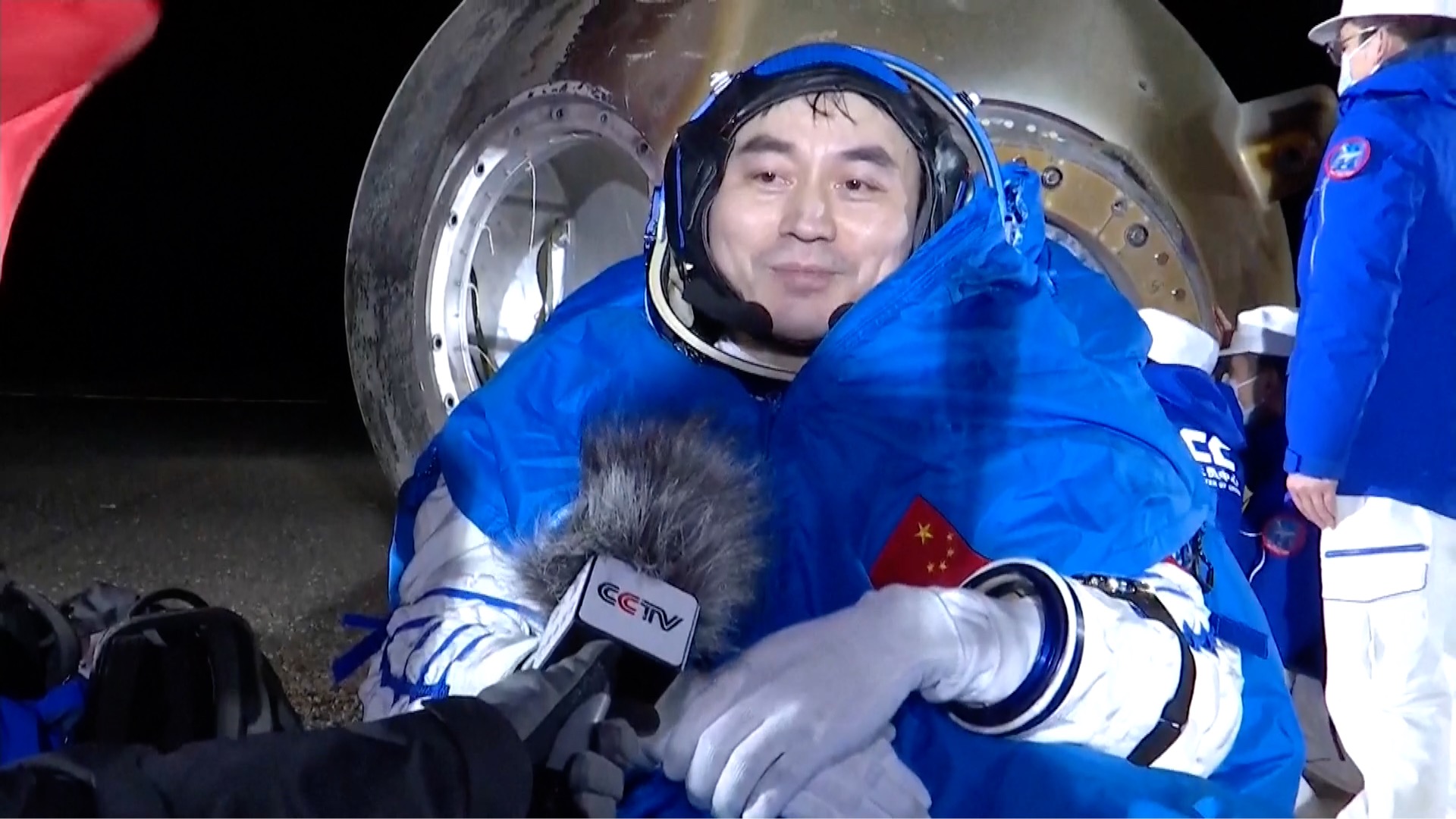
Shenzhou-18 spaceflight mission was the first one for Li Cong. He said the crew was united as one, cooperating seamlessly with the ground team to ensure two successful extravehicular activities (EVAs), while the in-orbit scientific experiments progressed smoothly as well.
“The exploration of space is limitless,” said Li, expecting to return to the vast space once again.
Li Guangsu, who also just completed his first flight mission with Shenzhou-18, said they had all enjoyed weightlessness in the vast, magical and beautiful space. Returning to Earth brings both excitement and a sense of nostalgia to leave space behind. “The biggest feeling at this moment is to feel proud of my great motherland,” said Li after coming out of the return capsule.
Multiple tasks completed during 192 days
China launched the Shenzhou-18 manned spacecraft on April 25. The spacecraft later conducted fast automated rendezvous and docked with the space station combination.
The three taikonauts stayed in orbit for 192 days, during which they carried out two EVAs. Their first EVA set a new record for the longest single spacewalk by taikonauts, lasting approximately 8.5 hours.
They also installed space debris protection devices on the space station, conducted several outbound cargo delivery missions and undertook tasks such as the installation, commissioning, maintenance and repair of equipment both inside and outside the space station.
In close cooperation with the ground crew, the taikonauts also carried out extensive space science experiments involving basic microgravity physics, space material science, space life science, space medicine and space technology.
One of their achievements was the creation of an “aquarium” to raise zebrafish in microgravity environment, marking China’s first in-orbit aquatic ecological research. The experiment involved studying the effects of the space environment on fish growth. In the experiment, zebrafish displayed abnormal swimming behaviors, including inverted swimming and circling under microgravity conditions. It also contributed to the understanding of material cycling in closed ecological systems in space.
The crew also conducted plant cultivation experiments to analyze changes in plant stem cell function and gene expression in a microgravity environment. The findings will aid in the development of crops that can thrive in outer space conditions.